

My Lenovo Yoga 3 Pro laptop had powerful hardware in a poorly ventilated chassis. However, you can safely assume that your battery temperature will be high if your processor is running hot. You’ll need to do some research to find one that’s compatible with your computer. There are similar manufacturer- and model-specific apps available for some Windows PCs. You can get a temperature snapshot reading off a MacBook’s battery with the Coconut Battery app. Lithium-ion batteries ideally shouldn’t exceed room-temperature and will irreversibly deteriorate faster in higher temperatures. You can prolong how long your battery will remain usable by lowering its temperature.
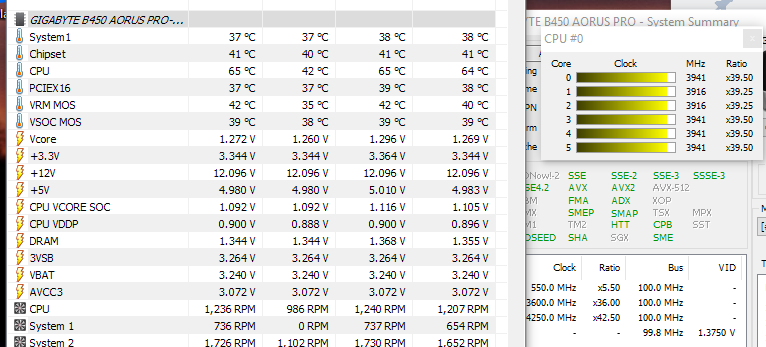
A rise in processor temperature will also lead to increased temperatures in other components including the battery. In small contained devices with poor heat exchange (like most laptops), this will spin up the fans but the temperature will also raise. However, boost mode also drains the battery quicker and can bring up the device temperature. It’s intended to finish short bursts of above-average workloads quickly.

Processor performance boost modes (“boost mode”), like Intel Turbo Boost or AMD Core Turbo, are designed to temporarily let the processor consume more energy in exchange for a temporary increase in processing speed. Yet, they’re crammed into small compartments with poor cooling inside our electronics. They don’t like being fully charged or discharged and they don’t like heat. They’ll only last a limited number of charge–discharge cycles. Lithium-ion batteries have a limited life-span and naturally deteriorate over time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
